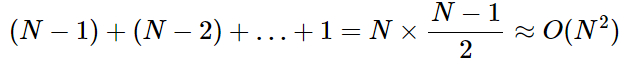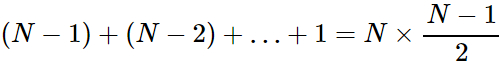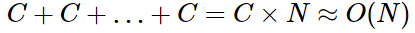2017年1月30日
部分文字列とRegExpの領域の冒険
本記事は、原著者の許諾のもとに翻訳・掲載しております。
パート1:小さな部分文字列はでき”ない”
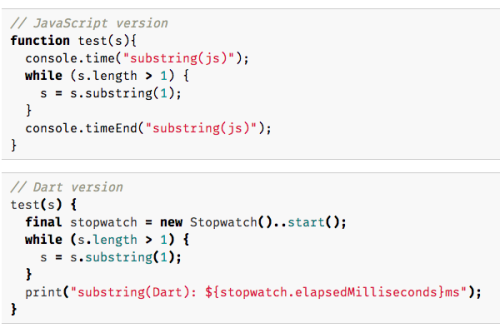
数週間前、Dart SDKに関して、 String.substring のパフォーマンスが非常に悪い というバグが報告されました。以下は、その問題と一緒に提出されたマイクロベンチマークの中心部分です。
// JavaScript version
function test(s){
console.time("substring(js)");
while (s.length > 1) {
s = s.substring(1);
}
console.timeEnd("substring(js)");
}// Dart version
test(s) {
final stopwatch = new Stopwatch()..start();
while (s.length > 1) {
s = s.substring(1);
}
print("substring(Dart): ${stopwatch.elapsedMilliseconds}ms");
}結果は、Dartバージョンでかなり悪くなっています。
$ dart substring.dart
benchmarking with string of length 25000
substring(Dart): 244ms
benchmarking with string of length 50000
substring(Dart): 949ms
benchmarking with string of length 100000
substring(Dart): 3709ms
$ node substring.js
benchmarking with string of length 25000
substring(js): 2.566ms
benchmarking with string of length 50000
substring(js): 2.308ms
benchmarking with string of length 100000
substring(js): 2.633ms見る方の経歴によっては、Dartでの実行時間が非線形増加を示していることにも驚くかもしれません。つまり、入力文字列のサイズを2倍(25000から50000)に増やすと、実行時間が4倍(244ミリ秒から949ミリ秒)に増えているのです。
dart --observe でベンチマークを実行して CPUプロファイル を Observatory で見てみると、意外ではない結果となりました。
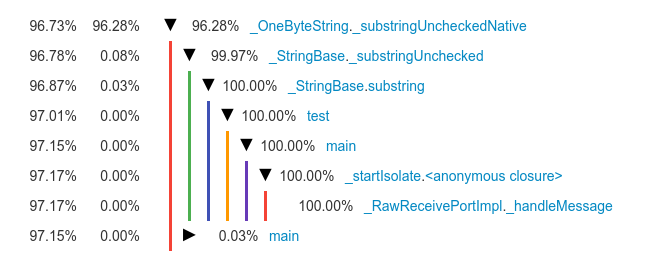
実行時間の大部分が、部分文字列の操作に費やされています。では、なぜDart VMの部分文字列はV8のよりも時間がかかるのでしょうか?実装が全く異なっているのに違いありません。そして、実際そうなっています。
Dart VMは、 String.substring(start, end) を非常に直接的な方法で実装しています。長さ end - start + 1 の新しい String オブジェクトを割り当て、この新しい文字列に文字列コンテンツをコピーします。形式的にいえば、これは O ( n ) の実装であり、 線形時間 としても知られています。部分文字列の長さに比例した演算量が必要になるということです。
ベンチマークの中心部分を見てみると、実行時間が 2次 成長を示した理由が明らかになるはずです。
while (s.length > 1) {
s = s.substring(1);
}文字列 s の初めの長さをNと仮定すると、ループの最初の反復で長さN−1の部分文字列が生成されます。次の反復で長さN−2の部分文字列が生成され、以後同様に続きます。最後の反復で長さ1の部分文字列が生成されます。ループに必要な演算は以下の数式で表されます。
これは、 N 2 に比例します。
[上記の数列を今まで見たことのなかった方は、ちょっと時間を取って、和の公式の導き方について考えてみることをお勧めします。解法がいかに単純で簡潔かが分かると、Webpackの設定との格闘をやめられるようになるかもしれません。数学の フリードリヒ・ガウス は、これを8歳の時に見事に理解していました。もちろん、ガウスがモダンなJavaScriptのエコシステムを前にした時に何をするかは、想像もつきませんが]
上記ループの計算量 O ( N 2 ) こそ、文字列の反復時に処理済みの部分をスライシングする方法が適さない理由を示しています。ただし、ランタイムが内部で”ちょっとした”マジックを使って、この特定のパターンを最適化できるのであれば、もちろん話は別です。V8はその最適化を行います。
V8のソースを調べてみると、何だか恐ろしくごちゃごちゃとした、様々な文字列表現があることが分かりました。それぞれ、特定のユースケース(索引付け、連結、スライシング)のための最適化です。
// The String abstract class captures JavaScript string values:
//
// Ecma-262:
// 4.3.16 String Value
// A string value is a member of the type String and is a finite
// ordered sequence of zero or more 16-bit unsigned integer values.
//
// All string values have a length field.
class String: public Name {
// ...
};
// The SeqString abstract class captures sequential string values.
class SeqString: public String {
// ...
};
// The OneByteString class captures sequential one-byte string objects.
// Each character in the OneByteString is an one-byte character.
class SeqOneByteString: public SeqString {
// ...
};
// The TwoByteString class captures sequential unicode string objects.
// Each character in the TwoByteString is a two-byte uint16_t.
class SeqTwoByteString: public SeqString {
// ...
};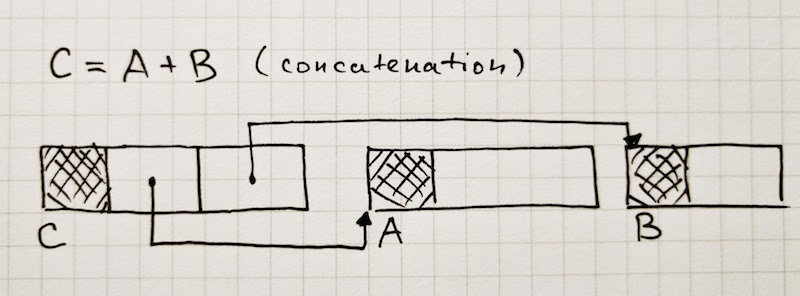
// The ConsString class describes string values built by using the
// addition operator on strings. A ConsString is a pair where the
// first and second components are pointers to other string values.
// One or both components of a ConsString can be pointers to other
// ConsStrings, creating a binary tree of ConsStrings where the leaves
// are non-ConsString string values. The string value represented by
// a ConsString can be obtained by concatenating the leaf string
// values in a left-to-right depth-first traversal of the tree.
class ConsString: public String {
// ...
};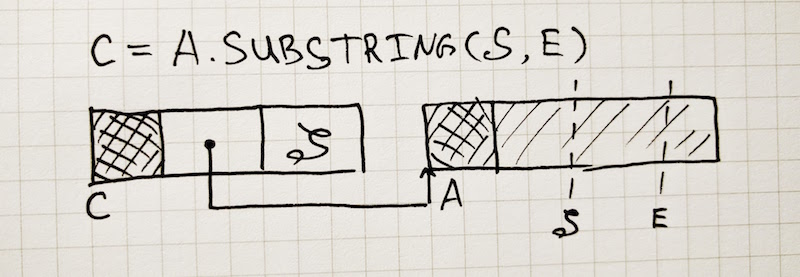
// The Sliced String class describes strings that are substrings of another
// sequential string. The motivation is to save time and memory when creating
// a substring. A Sliced String is described as a pointer to the parent,
// the offset from the start of the parent string and the length. Using
// a Sliced String therefore requires unpacking of the parent string and
// adding the offset to the start address. A substring of a Sliced String
// are not nested since the double indirection is simplified when creating
// such a substring.
// Currently missing features are:
// - handling externalized parent strings
// - external strings as parent
// - truncating sliced string to enable otherwise unneeded parent to be GC'ed.
class SlicedString: public String {
// ...
};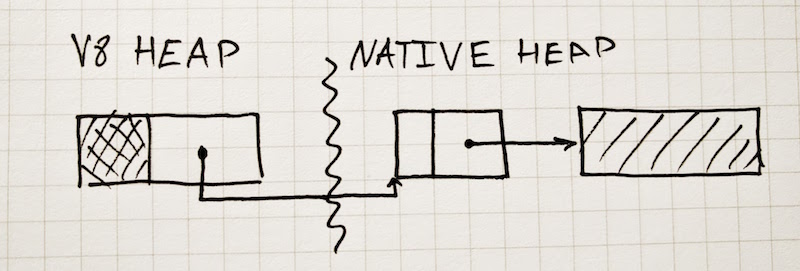
// The ExternalString class describes string values that are backed by
// a string resource that lies outside the V8 heap. ExternalStrings
// consist of the length field common to all strings, a pointer to the
// external resource. It is important to ensure (externally) that the
// resource is not deallocated while the ExternalString is live in the
// V8 heap.
//
// The API expects that all ExternalStrings are created through the
// API. Therefore, ExternalStrings should not be used internally.
class ExternalString: public String {
// ...
};
// The ExternalOneByteString class is an external string backed by an
// one-byte string.
class ExternalOneByteString : public ExternalString {
// ...
};
// The ExternalTwoByteString class is an external string backed by a UTF-16
// encoded string.
class ExternalTwoByteString: public ExternalString {
// ...
};JavaScriptコードで文字列値を見る時、実はこれらの表現が背後にあるわけですが、その時はいつでも、ランタイムはこれらの表現を切り替えて操作することができ、操作のパフォーマンスが向上するのであれば、ある表現から別の表現へ動的に移行することさえ可能です。
[他のJavaScriptランタイムも、ベンチマーク競争から生じた同じく複雑な表現階層を持ち、一般的な使用パターンのための最適化を志向しています。SpiderMonkeyの String.h や、JSCの JSString.h 、Chakraの ソース にある*String.hファイルをご参照ください]
様々なJavaScriptランタイムで使われている様々な文字列表現の違いを理解することは、通常、自分の書いた文字列操作コードが一定のパフォーマンスを示す理由を理解するための鍵となります。例えば、少し脱線して以下の例で考えてみましょう。
function strange() {
var s = "01234567891011121314";
for (var i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s += s[Math.floor(s.length / 2)];
}
return s;
}このコードは、SpiderMonkeyではV8の場合より60倍速く動きます。ただ残念ながら、その詳細について扱うのは本記事の範囲外です。
String.prototype.substring のマイクロベンチマークの話に戻りましょう。C++のレイヤとアセンブリをかき分けていくと、最終的に、 部分文字列操作を実装しているコード に到達するはずです。
// Note: this a cleaned up version of the original V8 code with some
// unimportant details removed for readablity.
Handle<String> Factory::NewProperSubString(Handle<String> str,
int begin,
int end) {
// If string is a cons-string produced as a result of concatenations
// flatten it to have a flat representation.
str = String::Flatten(str);
int length = end - begin;
if (length < SlicedString::kMinLength /* 13 */) {
// If resulting substring is small then simply allocate a new sequential
// string and fill it with characters.
if (str->IsOneByteRepresentation()) {
Handle<SeqOneByteString> result =
NewRawOneByteString(length).ToHandleChecked();
uint8_t* dest = result->GetChars();
String::WriteToFlat(*str, dest, begin, end);
return result;
} else {
Handle<SeqTwoByteString> result =
NewRawTwoByteString(length).ToHandleChecked();
uc16* dest = result->GetChars();
String::WriteToFlat(*str, dest, begin, end);
return result;
}
}
// Resulting substring is large enough to warrant sliced-string allocation.
// Instead of allocating sequential string and copying substring characters
// allocate a SlicedString object that contains a pointer to the
// original string, substring start offset and substring length.
int offset = begin;
// If input string is a SlicedString itself unwrap it.
if (str->IsSlicedString()) {
Handle<SlicedString> slice = Handle<SlicedString>::cast(str);
str = slice->parent();
offset += slice->offset();
}
// Create a slice.
Handle<SlicedString> slice = New<SlicedString>(...);
slice->set_hash_field(String::kEmptyHashField);
slice->set_length(length);
slice->set_parent(*str);
slice->set_offset(offset);
return slice;
}[V8では、1つの場所 だけ に実装されたものはないので、部分文字列の実装探しに迷える人は、さらに CodeStubAssembler::SubString を詳しく調べることになるかもしれません。これは、マシンコードにコンパイルされてSubStringスタブとして役立つTurboFanグラフを作成します。SubStringスタブは基本的に、上記C++ロジックへのファストパスを実装するものです]
このC++ロジックをDartに変換すると、以下のようになります。
class StringSlice /* implements String */ {
final String parent;
final int offset;
final int length;
StringSlice(this.parent, this.offset, this.length);
static substring(str, start, [end]) {
if (end == null) {
end = str.length;
} else if (end > str.length) {
throw "range error: end ${end} is greater than string length ${str.length}";
}
if (start < 0 || start >= end) {
throw "range error: start ${start} is out of range [0, ${end})";
}
final length = end - start;
if (str is StringSlice) {
start += str.offset;
str = str.parent;
}
return new StringSlice(str, start, length);
}
}
test(s) {
final stopwatch = new Stopwatch()..start();
while (s.length > 1) {
s = StringSlice.substring(s, 1);
}
print("substring(Dart): ${stopwatch.elapsedMilliseconds}ms");
}$ dart substring.dart
benchmarking with string of length 25000
substring(Dart): 3ms
benchmarking with string of length 50000
substring(Dart): 3ms
benchmarking with string of length 100000
substring(Dart): 1msこれがJavaScriptバージョンのおおよその動作であり、マイクロベンチマークで2次の計算量が観察されない理由が示されています。大まかにいえば、部分文字列操作は(入力文字列が単調だと仮定し、メモリ管理のオーバーヘッドを無視すると)一定時間を要します。したがって、
パフォーマンスが劇的に向上するのであれば、なぜDart VMで同様の最適化を実装しないのでしょうか。それは、この部分文字列最適化には危険な落とし穴があるからです。驚くべき メモリリーク を引き起こすのです。
function process(str) {
var small20CharToken = str.substring(0, 20);
return {token: small20CharToken};
}
var obj = process(gigantic10GbString);上記の obj は、わずか20文字のトークンではなく、10GBの入力文字列全体を保持します。なぜなら、このトークンの内部表現は、ソース文字列を指す SlicedString であるからです。わざとらしい例に見えるかもしれませんが、このようなメモリリークは本当に実際の場で起こりがちです。例えば、 three.js はこの問題を 回避しなければなりません 。ランタイムが見えないところで巧妙な最適化を行ってコードを速めることには、厄介な側面もあります。 Issue 2869 では、この問題のV8側での修正について経過をたどっていますが、2013年以来、実際的には何も起こっていません。その理由は恐らく、唯一のシンプルかつ確かな解決法は、スライシングされた文字列を完全に除去することだからでしょう。興味深いことに、これはまさにJavaが行っていたことです。Javaはかつて、親の String の char[] ストレージを部分文字列オブジェクトのために再利用することで、 O (1)時間での String.substring を実装していました。しかし、これは メモリリーク を引き起こし、 結局2012年に廃止されました 。V8の文字列スライスに関する経緯は、さらに不思議です。V8には元々、 文字列スライスがあり 、2009年に 廃止 されましたが、その後2011年に 復活 したのです。
以上のことは、本記事の道のりの 出発点となったDart SDKのバグ にとっては、少々厄介な問題です。実のところDart VMは、スライシングされた文字列による部分文字列最適化を実装しそうにありません。そこで私は、一体なぜ部分文字列のパフォーマンスが測定されているのかを探ることにしました。
パート2: less_dart の登場
冒頭のバグは、 less_dart が遅いことについての調査で見つかったものだと分かりました。 less_dart とは、 less.js のJavaScriptからDartへのポートです。
less_dart のベンチマークをObservatoryで見てみると、以下の結果になりました。
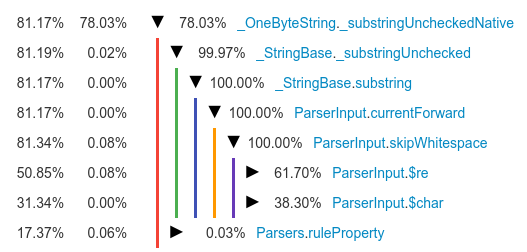
Lessパーサが、私なら勧めないことをまさに行っています。つまり、部分文字列操作で入力文字列の処理を繰り返しているのです。ソースを調べたところ、以下のコードが浮上し、部分文字列を使っている理由も明らかになりました。
$re(RegExp reg, [int index]) {
if (i > currentPos) {
current = current.substring(i - currentPos);
currentPos = i;
}
Match m = reg.firstMatch(current);
if (m == null) return null;
// ... skipped ...
}[コードはJavaScriptから逐語的にポーティングされていますので、 まさに同じコード がJavaScriptバージョンに存在します。そちらでは、準最適化が 有用な JavaScriptランタイムの存在によって隠れています]
Lessの作者は、カスタムレクサを書くのではなく正規表現を使って入力をパースすることに決めました。しかし、ES6以前の世界では RegExp で解析することは複雑でした。なぜなら、正規表現を使って 指定位置で マッチするかを簡単に調べることができなかったためですが、それこそ、文字列をたどってトークンに分割する際にレクサが行う必要のあることです。
function Lexer(str) {
this.str = str;
this.idx = 0;
}
Lexer.prototype.nextToken = function () {
if (this.idx == this.str.length)
return "eof";
else if (this.match(/\d+(?!\w)/))
return "number";
else if (this.match(/[a-zA-Z_]\w*/)) {
// note: names can't start with a digit
return "name";
} else if (this.match(/\s+/))
return "space";
else
throw "unexpected token";
};
// Try to match the given regexp at the current
// position (this.index) in the string.
// If match succeeds then advance position in the
// string past it and return the match object.
// Otherwise return null.
Lexer.prototype.match = function (re) {
// ???
}; match は、ES6で導入された RegExpの sticky フラグ をサポートするモダンなJavaScriptインタプリタなら、どれにでも容易に実装できます。
Lexer.prototype.match = function (re) {
re.lastIndex = this.idx;
var m = re.exec(this.str);
if (m != null) {
this.idx = re.lastIndex;
}
return m;
};
// Note: all regular expressions now need to have
// sticky bit set.
Lexer.prototype.nextToken = function () {
if (this.idx == this.str.length)
return "eof";
else if (this.match(/\d+(?!\w)/y))
return "number";
else if (this.match(/[a-zA-Z]\w*/y))
return "name";
else if (this.match(/\s+/y))
return "space";
else
throw "unexpected token";
};[フラグ y は、 Lex のAPIの一部である yylex にちなんで名付けられたようです(その技術はES7に含まれるも技術よりも高度なものでつくられた宇宙船 Lexx と混同しないように)。恐らく sticky という名前も、*yで終わるという理由で選ばれたのでしょう]
では、ES6以前のJavaScriptエンジンで match を実装する方法とは? 非常に単純なアプローチを取るとしたら、以下のようになるでしょう。
Lexer.prototype.match = function (re) {
re.lastIndex = this.idx;
var m = re.exec(this.str);
// No match at all or match at a wrong
// position
if (m === null ||
m.index !== this.idx) {
return null;
}
this.idx = re.lastIndex;
return m;
};
// Note: all regular expressions now need to have
// global bit set otherwise lastIndex will be
// ignored.
Lexer.prototype.nextToken = function () {
if (this.idx == this.str.length)
return "eof";
else if (this.match(/\d+(?!\w)/g))
return "number";
else if (this.match(/[a-zA-Z]\w*/g))
return "name";
else if (this.match(/\s+/g))
return "space";
else
throw "unexpected token";
};ですが、この方法は極めて非効率です。というのも、 match(/\d+/g) を呼び出すと基本的に、最初の数字列を探すために this.idx 以降を検索して、 this.idx で出現したマッチでなければ破棄することになるからです。
RegExp の機能にもう少し詳しい人であれば、以下のような最適化を考えるかもしれません。
// Note: all regexps have irrefutable pattern
// as an alternative "...|()" this guarantees
// that regexp engine won't attempt to match
// this expression at a different position because
// irrefutable pattern always matches.
Lexer.prototype.nextToken = function () {
if (this.idx == this.str.length)
return "eof";
else if (this.match(/\d+(?!\w)|()/g))
return "number";
else if (this.match(/[a-zA-Z]\w*|()/g))
return "name";
else if (this.match(/\s+|()/g))
return "space";
else
throw "unexpected token";
};
Lexer.prototype.match = function (re) {
re.lastIndex = this.idx;
var m = re.exec(this.str);
// No match at all or an empty match.
if (m === null || m[0] === "") {
return null;
}
this.idx = re.lastIndex;
return m;
};しかし、 match を実装するもっと一般的かつ直接的な方法は、 substring と アンカーを付けた 正規表現を使うものでしょう。
Lexer.prototype.match = function (re) {
var m = re.exec(this.str);
if (m !== null) return null;
// Slice away consumed part of the string.
this.str = this.str.substring(m[0].length);
return m;
};
// Note: all regular expressions now need to
// be anchored at the start.
Lexer.prototype.nextToken = function () {
if (this.str.length === 0)
return "eof";
else if (this.match(/^\d+(?!\w)/))
return "number";
else if (this.match(/^[a-zA-Z]\w*/))
return "name";
else if (this.match(/^\s+/))
return "space";
else
throw "unexpected token";
};これはまさしく、 less.js と less_dart にあるコードです。 less.js にとっては幸いなことに、V8ランタイムは String.prototype.substring を O (1)の演算として実装し、 less_dart にとっては不運なことに、Dart VMは O (1)の演算として実装していません。
Dart VMが実装 している のは、 RegExp.matchAsPrefix のメソッドです。これは基本的に、指定された正規表現についてstickyなマッチを指定位置で実行するものです。バンザイ!☺
しかし、 less_dart コードに必要な変更を施したところ、実際には何倍も遅くなってしまいました。うーん。☹
結局、VMのRegExp実装の内部に、ちょっとした TODO があったことが分かりました。
Match matchAsPrefix(String string, [int start = 0]) {
// ...
// Inefficient check that searches for a later match too.
// Change this when possible.
List<int> list = _ExecuteMatch(string, start);
if (list == null) return null;
if (list[0] != start) return null;
return new _RegExpMatch(this, string, list);
}明らかに、この解決法は、V8がstickyフラグを実装しているのと同じやり方で RegExp.matchAsPrefix を実装することでVMを修正する、というものでした。これは、Dart VMが基本的に、V8と同じく Irregexp と呼ばれる 正規表現エンジン を使っているので、ややシンプルになっています。
[Dart VMポートをIrIrRegexpと呼ぶべきだったかもしれません。なぜなら、Dart VMは、RegExp特有の中間表現(IR)をマシンコードに変換する代わりに、マシンに依存しないIRにまで変換し、その処理をジェネリックなコンパイラパイプラインに任せるからです。これによって、マシン特有の正規表現関連バックエンドコードをポーティングしなくても、IrregexpをDart VMに組み込むことができたのです]
そこで私は、オリジナルのIrregexpで sticky フラグの実装を推進していた1人である Erik Corry に直接相談してみました。そして、 sticky フラグをDart VMにポーティング してみました。その際に、V8の sticky の実装における非常に小さなバグを 発見し、修正 しました。
RegExp.matchAsPrefix が効率的な形で実装されたので、私がless_dartの 修正 を行った結果、期待されたパフォーマンス改善が実現して、 less_dart と less.js が互角の状態になりました。
パート3:RegExpの落とし穴
できればこのポジティブな雰囲気で本記事を終えたかったのですが、ソースコードをトークン化するために正規表現を使うという一般的な話に戻りたいと思います。
その実現に際して非常に重要な点は、確かに正規表現は解析に便利な方法であるとはいえ、決して効率的な方法ではないということです。関係している抽象化レイヤがとにかく多すぎるのです。
前に試したように、正規表現でのトークン化とそのベンチマークテストを ("aaaaa aaaa ".repeat(50) + "10 ").repeat(10000) のような単純な文字列で実行してみると、以下のようなパフォーマンス数値が得られます。
# Naive tokenizer that just uses global regexps with lastIndex.
$ node tokenize-global.js
processed 2020001 tokens in 987ms
# Tokenizer that is using a global regexps with an irrefutable pattern
# to prevent searching for regexp match forward.
$ node tokenize-global-irrefutable.js
processed 2020001 tokens in 471ms
# Tokenizer that uses anchored regexps and substring to slice
# away the processed part of the string.
$ node tokenize-substring.js
processed 2020001 tokens in 393ms
# Tokenizer that uses sticky regexps.
$ node tokenize-sticky.js
processed 2020001 tokens in 295ms速度を上げられるでしょうか? 抽象化レイヤを取り払い、完全に手動でやってみましょう。
function Lexer(str) {
this.str = str; // Input string
this.idx = 0; // Current position within the input.
this.tok = null; // Last parsed token type (number, name, space)
this._tokStart = this._tokEnd = 0; // Last parsed token position.
}
// Lazy getter for the token value - to avoid allocating substrings
// when not needed.
Object.defineProperty(Lexer.prototype, "val", {
get: function () {
return this.str.substring(this._tokStart, this._tokEnd);
}
});
function isDigit(ch) {
return 48 /* 0 */ <= ch && ch <= 57 /* 9 */;
}
function isAlpha(ch) {
ch &= ~32;
return 65 /* A */ <= ch && ch <= 90 /* Z */;
}
function isIdent(ch) {
return isAlpha(ch) ||
isDigit(ch) ||
ch === 95 /* _ */
}
function isSpace(ch) {
return ch === 9 /* \t */ ||
ch === 10 /* \n */ ||
ch === 13 /* \r */ ||
ch === 32 /* space */;
}
Lexer.prototype.nextToken = function () {
if (this.idx >= this.str.length) {
return "eof";
}
this._tokStart = this.idx;
var ch = this.str.charCodeAt(this.idx++);
if (isDigit(ch)) {
while (this.idx < this.str.length &&
isDigit(this.str.charCodeAt(this.idx))) {
this.idx++;
}
if (this.idx < this.str.length && isIdent(this.str.charCodeAt(this.idx))) {
throw "unexpected token";
}
this.tok = "number";
} else if (isAlpha(ch) || ch === 95) {
while (this.idx < this.str.length &&
isIdent(this.str.charCodeAt(this.idx))) {
this.idx++;
}
this.tok = "name";
}
else if (isSpace(ch)) {
while (this.idx < this.str.length &&
isSpace(this.str.charCodeAt(this.idx))) {
this.idx++;
}
this.tok = "space";
}
else
throw `unexpected token '${ch}'`;
this._tokEnd = this.idx;
return this.tok;
};別用途の際に私が使ったものと全く同じベンチマークで、このトークナイザのベンチマークテストを実行します。
function benchmark() {
var seq = ("aaaaa aaaa ".repeat(50) + "10 ").repeat(10000);
var l = new Lexer(seq);
var start = Date.now();
var cnt = 0;
do {
var tok = l.nextToken();
cnt++;
} while (tok != "eof");
var end = Date.now();
console.log(`processed ${cnt} tokens in ${end - start}ms`);
}すると、以下の結果が出ました。
$ node tokenize-manual.js
processed 2020001 tokens in 50msこのことから分かる重要なポイントは、 作業量が減ればプログラムははるかに速くなる ということです。例えば、この手動トークナイザは、部分文字列オブジェクトのトークンへの割り当ては行わず、単純に文字列をたどるものです。しかし、 var val = l.val; をベンチマークのループ内に追加してこの無意味な割り当てを強制するようにすると、やはり、RegExpベースのパーサよりはるかにパフォーマンスが良いことが分かります。
$ node tokenize-manual.js
processed 2020001 tokens in 98ms以下にDartにおける同種のレクサベンチマークを挙げておきます。
class Lexer {
final String str; /// Input string.
int idx = 0; /// Current position within the str.
Lexer(this.str);
Token tok; /// Last processed token type.
/// Last processed token value.
String get val => str.substring(_tokStart, _tokEnd);
/// Beginning and end positions of the last processed token.
var _tokStart = 0;
var _tokEnd = 0;
Token nextToken() {
if (idx == str.length) return Token.End;
_tokStart = idx;
final ch = advance();
if (isDigit(ch)) {
while (isDigit(currentChar)) idx++;
if (isIdent(currentChar)) {
throw "unexpected token";
}
tok = Token.Number;
} else if (isAlpha(ch) || ch == _) {
while (isIdent(currentChar)) idx++;
tok = Token.Name;
} else if (isSpace(ch)) {
while (isSpace(currentChar)) idx++;
tok = Token.Space;
} else {
throw "unexpected token";
}
_tokEnd = idx;
return tok;
}
int advance() => str.codeUnitAt(idx++);
int get currentChar => idx < str.length ? str.codeUnitAt(idx) : 0;
static final ZERO = '0'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final NINE = '9'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final A = 'A'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final Z = 'Z'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final _ = '_'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final SPACE = ' '.codeUnitAt(0);
static final LF = '\n'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final CR = '\r'.codeUnitAt(0);
static final TAB = '\t'.codeUnitAt(0);
static isDigit(ch) => ZERO <= ch && ch <= NINE;
static isAlpha(ch) {
ch = ch & ~32;
return (A <= ch && ch <= Z);
}
static isSpace(ch) => ch == SPACE || ch == LF || ch == CR || ch == TAB;
static isIdent(ch) => isAlpha(ch) || isDigit(ch) || ch == _;
}
enum Token {
Number, Name, Space, End
}
benchmark() {
var seq = ("aaaaa aaaa " * 50 + "10 ") * 10000;
var l = new Lexer(seq);
final stopwatch = new Stopwatch()..start();
var tok, val;
var cnt = 0;
do {
tok = l.nextToken();
val = l.val; // Force substring allocation.
cnt++;
} while (tok != Token.End);
print('processed ${cnt} tokens in ${stopwatch.elapsedMilliseconds}ms');
return val;
}Dart VMは、このコードでなかなかのパフォーマンスを見せました。
$ dart tokenize.dart
processed 2020001 tokens in 67msまとめると、パフォーマンスに関する総合的なアドバイスは以下のようになります。
- RegExpを解析のために使う時は、Nodeでは sticky フラグを、Dart VMでは
RegExp.matchAsPrefixを使う。 - 正規表現を使う代わりにレクサを自作できないか、よく検討してみる。
- プログラムの作業量が減れば減るほど実行は速くなる。関係している抽象化レイヤが減れば減るほど、プログラムの実際の作業量を導き出してそれを減らすのが簡単になる。
株式会社リクルート プロダクト統括本部 プロダクト開発統括室 グループマネジャー 株式会社ニジボックス デベロップメント室 室長 Node.js 日本ユーザーグループ代表
- X: @yosuke_furukawa
- Github: yosuke-furukawa